Vision and Strategy
Sustainability Vision
Samsung Electro-Mechanics has established a vision for sustainable management to create value for stakeholders and enhance sustainable growth and corporate value. We will fulfill our social responsibilities for a clean global environment and strive to ensure the health and happiness of all employees. We will also relentlessly take on challenges despite external uncertainties in pursuit of sustainable growth.
Sustainability Strategy
Samsung Electro-Mechanics creating future values by prioritizing the realization of environmental responsibility, the pursuit of happiness among members of society, and sustainable growth based on the ESG mission "Sustainable Challenges for a Better Planet & Life".
-
Planet
Dedicated to creating a clean and sustainable environment for future generations
- Climate Action
- Efforts to transition into 100% renewable energy by 2050
- 100% conversion of business vehicles to electric vehicles by 2030
- Continuous reduction of energy consumption
- Operation of Green Business Sites
- Obtaining 'Zero Waste-to-Landfill' certification for all business sites by 2025
- Expanding the company-wide reuse of water
- Maintaining on average 30% lower levels compared to the standards mandated by air and water pollutants laws and regulations
- Product Stewardship
- Acquisition of carbon footprint certifications for more products
- Compliance with global substance standards RoHS and REACH SVHC
-
People
Committed to fostering mutual growth with our members and creating a happy society
- Labor and Human Rights
- Maintaining an organizational health index over 70 points by 2030
- Continuous increase in female leaders and establishment of a diversity management system
- Continuously achieving zero serious accidents
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Expanding support for youth education (Blue Elephant)
- Encouraging employees' talent donation and promoting donation culture (Sharing Kiosks)
- Customers and Suppliers
- Creating customer value through realizing the world-class quality
- Sharing our vision with customers and strengthening communication in both way
- Strengthening Field-oriented support and training assistance for suppliers
-
Progress
Pursuit of
unwavering growth through constant challenges- Governance Structure
- Maintaining the ratio of female independent directors as more than 50%
- Enhancing the board of directors' expertise and diversity
- Maintaining the ratio of independent directors as more than 50%
- Ethical Management
- Preventing corruption through fraud prevention training for employees
- Strengthening compliance inspections and monitoring system, and implementing compliance training for employees
- Establishing a response system against security threats in headquarters and overseas business sites
- Creating Economic Value
- Improving product competitiveness and securing future technologies
- Maintaining market leadership in material and component technology
Sustainability Governance
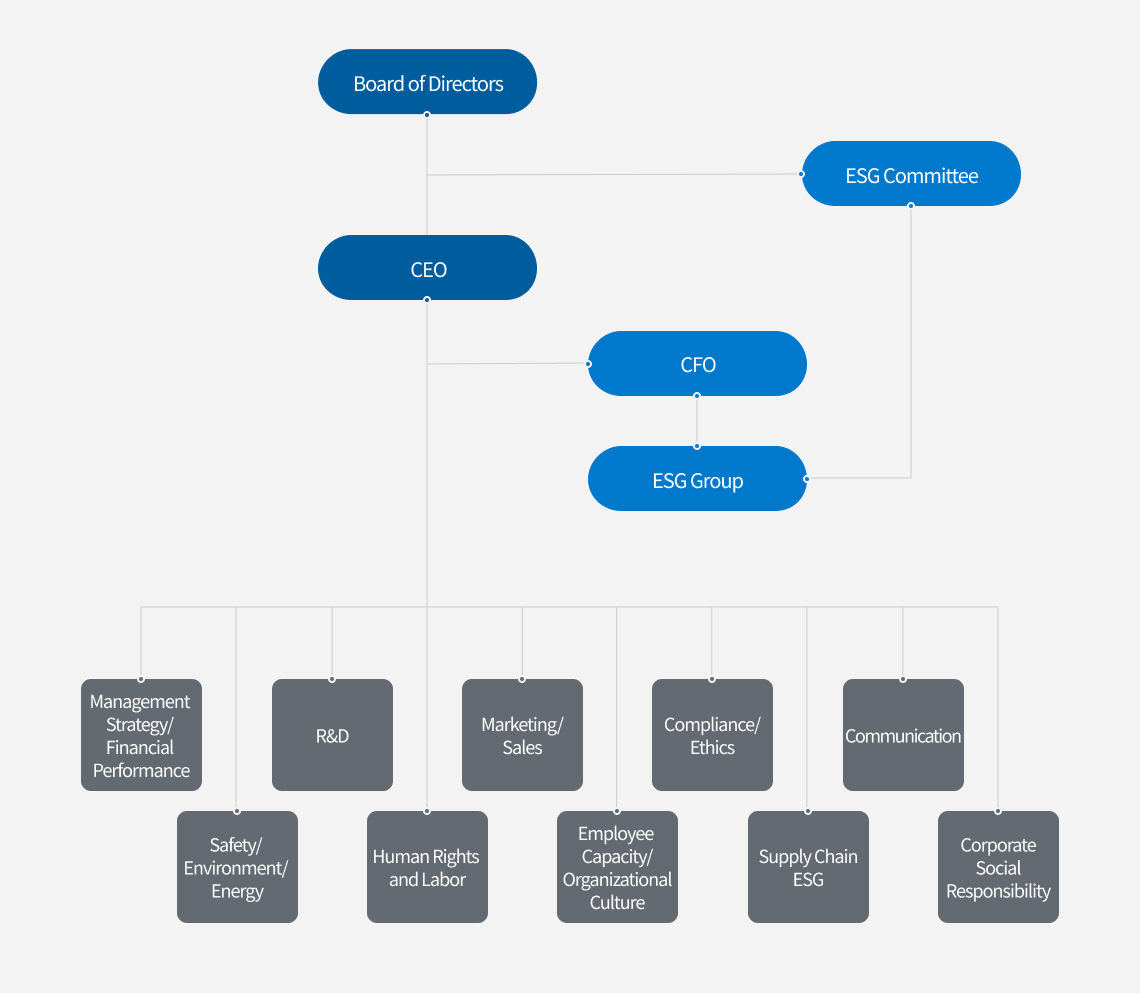
- Board of Directors
-
CEO
- CFO
-
ESG Group
- ESG Committee
-
- Management Strategy/ Financial Performance
- Safety/ Environment/ Energy
- R&D
- Human Rights and Labor
- Marketing/Sales
- Employee Capacity/ Organizational Culture
- Compliance/ Ethics
- Supply Chain ESG
- Communication
- Corporate Social Responsibility
ESG Committee
In October 2021, Samsung Electro-Mechanics established the ESG Committee under the Board of Directors. As the highest decision-making body, the ESG Committee promotes major ESG projects and reviews ESG disclosures to ensure that Samsung Electro-Mechanics fulfill its social responsibilities. The committee consists of four independent and two inside directors. In 2022, the company appointed Lee Yun-jeong, an environmental lawyer at Kim& Chang, as an independent director to improve the diversity and expertise of the board.
ESG Group
Samsung Electro-Mechanics operates the ESG Group as a department directly under the CFO in order to respond to ESG issues based on a strong cooperative system. The ESG Group regularly reviews the company's ESG strategies, policies, and major issues. It also handles key ESG tasks, inquiries from ESG rating agencies, and ESG disclosures through systematic collaboration with business units. In addition, the group monitors global and industry-related trends and strategic directions related to sustainability, addresses the latest issues, and drives sustainable development through active communication with internal and external stakeholders.
Stakeholder Communication
Samsung Electro–Mechanics values open communication with various interest groups. Through transparent corporate management and mutual trust opinions are actively obtained. These opinions are actively reviewed, applied in different sustainable management policies and made public through domestic and foreign channels.
Stakeholder Communication
- Customers
- Business Partners
- Employees
- Communities
- Environment
- Shareholders
Materiality Analysis
Samsung Electro-Mechanics conducts materiality analysis to identify sustainability issues that are critical to our stakeholders, including customers and investors, and to develop appropriate response strategies. Through materiality analysis, we identify key issues that we need to address by identifying the opportunities and risks faced by the company in each of our stakeholders’ areas of interest.
Materiality Analysis Process
-
- STEP 1 Form a pool of ESG issues
- ESG disclosure guidelines
(GRI, SASB, etc.) - Korean and overseas ESG rating agencies
(DJSI, CDP, MSCI, etc.) - Issues based on our ESG strategies
-
- STEP 2Analyze the issues
- (Social/environmental impact) stakeholder survey, media analysis, etc.
- (Financial impact) analysis of finance-related ESG guidelines (SASB, TCFD, etc.) and rating agencies (DJSI, MSCI etc.), stakeholder surveys, etc.
-
- STEP 3 Derive key issues
- Derive key issues by analyzing social, environmental, and financial impacts
-
- STEP 4 Report the issues
- Reflect them in the sustainability report
Risk Management
Internal Accounting Management
For the purpose of transparency, accounting information and for the proof of trustworthiness of the information disclosed among our stakeholders, Samsung Electro-Mechanics operates under an internal audit management system. Not only is the financial reported by the internal accountant at Samsung Electro-Mechanics, but there is also a much broader sense of an audit system that meets global standards in management of policies.
This helps us to prepare for any potential business risks, including CSR related issues, environment related regulations, conflicts on minerals management and environmental friendliness evaluations and more.
Business Continuity Management
Samsung Electro-Mechanics contributes to sustainable growth by ensuring a stable supply of products and services to customers based on the continuity of production activities. We have established the business continuity management in preparation for business suspension due to unexpected accidents.
Samsung Electro-Mechanics created scenarios to respond to crises caused by major accidents including fire and blackouts to secure business continuity. Periodic training and education on the business continuity procedure is conducted We categorize major stakeholders including internal/external customers, business partners and communities and maintain communication through stakeholder analysis.
Climate Change
Samsung Electro-Mechanics put in place a decision-making process to respond to the emission-trading scheme
by operating the Climate Strategy Committee and regularly monitoring the financial impact resulting from the emission right trading.
Site-specific annual safety check is carried out by an external agency, enabling comprehensive risk assessment and management of assets including on-site buildings,
facilities and machinery occurring due to natural disasters.
As such, we do the utmost to maintain stable business activities.
Information Protection
We prescribed information security regulations and implementation guidelines to protect Samsung Electro-Mechanics’s critical information and assets, and operate physical and technical protection measures to abide by them. This helps us to maintain optimized sites in security through periodic inspection and improvement activities. Thanks to close business ties with related agencies outside, we explore industrial security trends and information leakage scenarios through preventive programs to safeguard against security accidents.
Tax Risk
Samsung Electro-Mechanics fulfills the obligations on tax filing and payment of taxes by complying with tax laws of local countries as prescribed in Samsung Electro-Mechanics’s tax payment management guideline. To this end, we maintain transparent relationships with tax authorities in local countries where local subsidiaries of Samsung Electro-Mechanics belong, help with career management of personnel in local subsidiaries, and proactively utilize external specialists including accountants. Samsung Electro-Mechanis do not transfer value generated from business activities to low-tax jurisdictions such as tax havens for tax avoiding purposes. In particular, we maintain fair trading prices when dealing with third parties and special parties in accordance with each domestic transaction laws. Also, we undertake transfer pricing using the arm’s length principle.
Taxpaying Management Guideline
Principle: Compliance with the HQ and tax laws of local countries
- 1. All laws and regulations shall prioritize accounting standards and tax laws of the HQ and local countries.
- 2. Parties involved shall recognize differences between tax laws in each country, comply with tax laws in all transactions, and implement tax filing and tax paying obligations. we do not use secrecy jurisdictions or so-called "tax havens” for tax avoidance, and do not transfer value created to low tax jurisdictions.
- 3. Employees in charge of tax payment at local subsidiaries shall maintain transparent relationships with the tax authorities in each country and strive to prevent tax risks.
- 4. Management of internal personnel and utilization of external specialists must be maximized to comply with tax laws in local countries of overseas subsidiaries and prevent tax risks.
- 5. In the case of transactions between related parties, such as the headquarter and overseas business sites, the risk of obtaining a proper profit margin is measured through a transfer price review by external experts. We obtain relevant reports to respond to tax risks that may arise in the future.
- 6. All transactions are based on commercial substance(Prohibition of tax structure without commercial substance), and related qualifications are documented and kept. We meet the payment deadlines for all of our profits and fulfill our tax obligations.

